Contemporary Technical Analysis of SSL/TLS Certificates: Architecture, Validity, Algorithms, Market Landscape & Use-Case Taxonomy
SSL/TLS certificates underpin digital trust by binding cryptographic keys to verified identities. This paper surveys the state of the art in mid-2025, focusing on functional purpose, current and forthcoming validity limits, certificate classes, cryptographic construction, commercial and community certificate-authority (CA) offerings, and the expanding range of industrial use cases. History is deliberately excluded; the lens remains firmly on today’s engineering and governance realities.
Overview
Actual Purpose of an SSL/TLS Certificate
An SSL/TLS certificate is a digitally signed X.509 object that authenticates the endpoint of a network connection and bootstraps an encrypted channel. During the TLS handshake it allows the client to (a) verify the server’s identity against a trust anchor and (b) negotiate symmetric keys that provide confidentiality and integrity for the session. When mutual authentication (mTLS) is used, the same mechanism authenticates both peers.en.wikipedia.orgejbca.org
Latest Validity Limits and the Rationale for Shortening
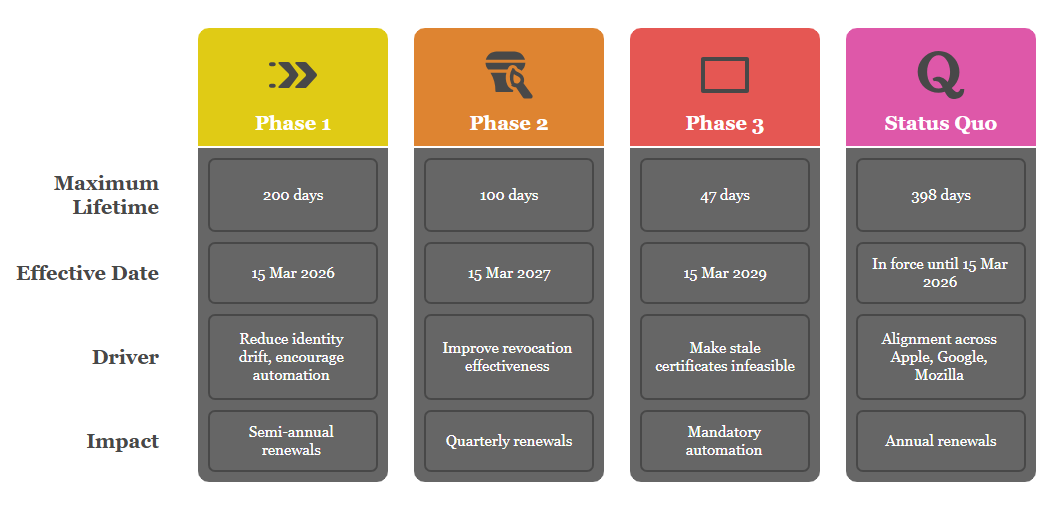
The schedule above was adopted by CA/B Forum Ballot SC-XX in April 2025 after Apple’s proposal won majority support; Google’s earlier 90-day vision folded into the final timetable. Shorter lifetimes compensate for weak revocation mechanisms and ensure organisational details are re-verified frequently.digicert.comglobalsign.com
Engineering takeaway: Manual renewal processes will be unsustainable well before 2029; ACME-based or agent-based automation should be budgeted now.
Certificate Types and Categories
DV (Domain), OV (Organisation), EV (Extended)
- Validation Effort: DV: domain-control only; OV: business registry check; EV: rigorous legal & physical vetting
- Typical Use-Cases: DV: blogs, SaaS micro-sites; OV: corporate portals; EV: high-risk transactions
- Why They Matter: Higher assurance levels add brand trust and liability warranties.digicert.comserverion.com
Single-Domain, Wildcard, Multi-Domain/SAN
- Validation Effort: DV: domain-control only; OV: business registry check; EV: rigorous legal & physical vetting
- Typical Use-Cases: Wildcard: micro-services on *.example.com; SAN: global web estate
- Why They Matter: Allows cost-efficient coverage of large host sets.
Public-trust TLS, Private PKI, Short-Lived (≤7 days)
- Validation Effort: Short-lived certs remove need for revocation; private PKI enables internal mTLS
- Typical Use-Cases: DevOps, IoT fleets, service meshes
- Why They Matter: Tailored validity and trust roots optimise security versus management overhead.
Code-Signing, S/MIME, Document Signing, IoT Device Identity
- Validation Effort: OV/EV or Qualified vetting
- Typical Use-Cases: Supply-chain security, e-mail, e-signatures, industrial sensors
- Why They Matter: Bind cryptographic identity to software, people or devices.
Cryptographic Foundations
Public-Key Algorithms
- RSA-2048/3072/4096 – still dominant for backwards compatibility.
- Elliptic-Curve (ECDSA P-256/P-384) – smaller keys, faster handshakes, browser-mandated for mobile performance.
- EdDSA (Ed25519/Ed448) – starting to appear in ACME clients and some modern CAs.
- Hybrid PQC (X25519-Kyber, RSA-Dilithium test roots) – pilot projects anticipating NIST standardisation 2027+.00f.netcrypto.stackexchange.com
Key-Exchange Mechanisms
- ECDHE + RSA/ECDSA (TLS 1.2) – provides forward secrecy.
- TLS 1.3 X25519 / secp256r1 – mandatory forward secrecy and 1-RTT handshake.learn.microsoft.com
Symmetric Ciphers (TLS 1.3) – defined as AEAD-only suites
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 (selected automatically on ARM/mobile)
- TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256 (IoT constrained devices)
Hash & Signature Algorithms
- SHA-256 / SHA-384 – default digest algorithms.
- RSA-PSS / ECDSA – signature schemes reflected in certificate’s SignatureAlgorithm field.
Note: Legacy CBC, 3DES and RC4 suites are forbidden by RFC 8996 and major browser root programs.
Commercial vs Free Certificate Ecosystem
Key Commercial CAs (mid-2025 market snapshot)
CA: DigiCert
Market Strengths: Quantum-ready roadmap; enterprise CLM.
Notable Developments: Leading role in 47-day ballot. digicert.com

CA: Sectigo (incl. Entrust public CA acquired Feb 2025)
Market Strengths: Broad SKU portfolio; aggressive pricing.
Notable Developments: Acquisition doubled enterprise base. wsj.com

CA: GlobalSign
Market Strengths: Early ACME support; IoT PKI
Notable Developments: Advocacy for 90-day lifetimes. globalsign.com

CA: GoDaddy
Market Strengths: Mass-market SSL with hosting bundles
Notable Developments: High retail visibility.coherentmarketinsights.com

CA: IdenTrust / Certum / SwissSign
Market Strengths: Specialist sectors (FedRAMP, eIDAS).
Notable Developments: Niche assurance programs.w3techs.com



Free CAs
- Let’s Encrypt – automates DV issuance (90-day default) via ACME; dominates 62 % of active certificates.letsencrypt.orgsci-tech-today.com
- ZeroSSL / Buypass Go SSL – alternative ACME-compatible DV providers.
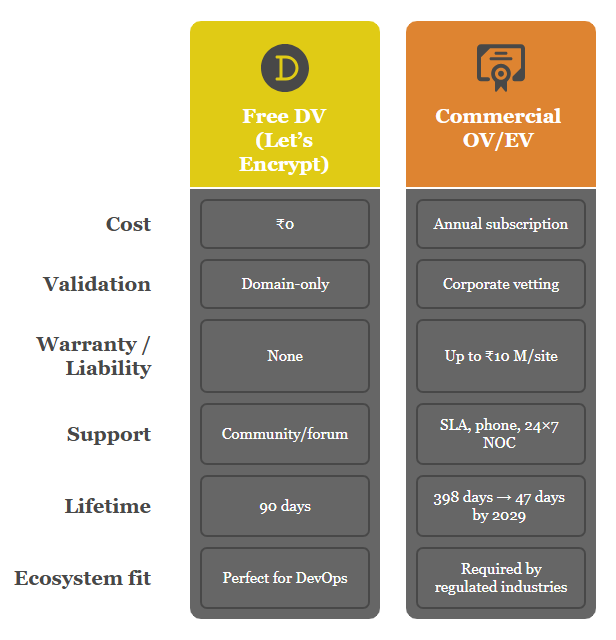
Recommendation: Adopt free DV where identity assurance is non-critical and automation is in place; retain commercial OV/EV for regulated workloads, brand trust requirements, or high indemnity needs.globalsign.commilesweb.com
Use-Case Spectrum for SSL/TLS Certificates
Domain
Description & Example
Web & SaaS
HTTPS for e-commerce, CMS, CDN edge.
API & Micro-services
mTLS between Kubernetes pods, service meshes (Istio, Linkerd).
Email Transport
STARTTLS for SMTP, implicit TLS for IMAPS & POP3S, preventing downgrade attacks.
Zero Trust Network Access
Client certificates authenticate users/devices without passwords.
IoT Device Identity
X.509 credentials burnt into firmware for sensor-to-cloud telemetry.
Industrial OT & SCADA
Secure Modbus/TCP over TLS gateways to meet IEC-62443.
VPN & Remote Desktop
TLS-based VPNs (OpenVPN, WireGuard TLS mode) and RDP-TLS channel binding.
Payment & FinTech
PCI-DSS mandates TLS 1.2+ with strong ciphers for cardholder data.
Regulated e-Signature & Document Integrity
Qualified Website Authentication Certificates (QWAC) and Adobe AATL chains.
Compliance Telemetry
HTTPS for e-commerce, CMS, CDN edge.
Conclusion
The SSL/TLS certificate ecosystem is transitioning from static, multi-year artefacts to highly ephemeral, automatically managed credentials. Driving factors include (a) aggressive validity reductions culminating in 47-day lifetimes, (b) TLS 1.3’s lean, AEAD-only cipher model, and (c) the rise of DevOps, IoT and zero-trust architectures that demand ubiquitous machine identity. Engineers should therefore:
- Automate discovery, issuance and renewal using ACME or CLM platforms.
- Standardise on TLS 1.3 and ECDSA certificates where possible for performance and forward secrecy.
- Segment use cases: reserve OV/EV certificates for high-stakes transactions and leverage free DV for commodity endpoints.
- Plan for post-quantum readiness by evaluating hybrid X.509 profiles as they mature.
The organisations that adapt now will avoid service-outage headlines when 100-day—and later 47-day—lifetimes become mandatory.
